Servo motors are versatile devices used in various applications, primarily for controlling the position of an object. They are pivotal in robotics, model airplanes, automotive systems, and more, providing precise and controlled movements.
Servo Motors
Servo Motors
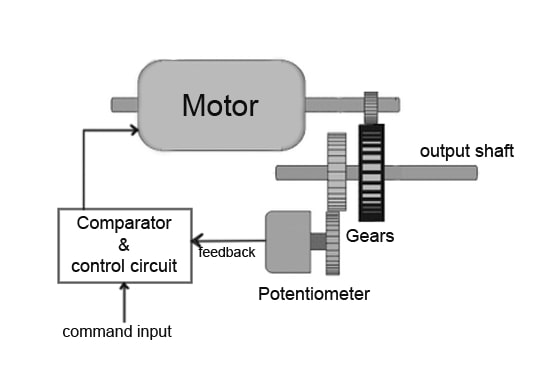
A servo motor is a rotary actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. It operates on the principle of a closed-loop control system, where feedback from the motor is continuously compared with the desired position. This feedback loop ensures accurate and controlled movement.
Price of Servo Motors
The price of servo motors varies based on factors like torque, size, and brand. Higher torque and larger-sized servo motors generally come at a higher cost. It's advisable to consider your project requirements and budget constraints when choosing a servo motor.
Tips for Buying Servo Motors
- Torque Requirements: Determine the required torque for your application. Servo motors come in various torque ratings, so selecting one with the appropriate torque ensures optimal performance.
- Size and Weight: Consider the physical dimensions and weight of the servo motor. Ensure it fits within the constraints of your project, especially if space is a critical factor.
- Feedback System: Choose a servo motor with the appropriate feedback system. Common types include encoder feedback and resolver feedback, each offering specific advantages in terms of precision and reliability.
- Speed and Acceleration: Evaluate the speed and acceleration requirements of your application. Different servo motors have varying speed capabilities, so select one that aligns with your project's needs.
- Power Supply Compatibility: Check the compatibility of the servo motor with your power supply. Ensure that the voltage and current requirements match the available power source.
Types of Servo Motors
- Analog Servo Motors: Analog servo motors operate based on an analog control signal. They are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for applications with moderate precision requirements. Common models include Hitec HS-311 and Futaba S3003.
- Digital Servo Motors: Digital servo motors utilize digital control signals, providing enhanced precision, accuracy, and rapid response. They are ideal for applications demanding high performance. Popular models include Savox SC-1258TG and Hitec HS-5645MG.
- Brushless DC Servo Motors: Brushless DC servo motors offer improved efficiency and longevity compared to their brushed counterparts. They are commonly used in applications requiring continuous rotation. Notable models are Tekin T-360 and Castle Creations 1512.
- High-Torque Servo Motors: High-torque servo motors are designed to deliver greater force, making them suitable for applications with demanding torque requirements. Examples include TowerPro MG996R, Power HD Storm-4 and Savox SV-1270TG.
- Micro Servo Motors: Micro servo motors are compact and lightweight, ideal for small-scale applications where space is limited. Common models include TowerPro SG90, SG92R and EMAX ES08AII.
- Industrial Servo Motors: Industrial servo motors are engineered for heavy-duty applications, providing robust performance in challenging environments. Notable models are Siemens 1FK7 and Yaskawa SGM7D.
- Robotics Servo Motors: Robotics servo motors are tailored for precise control in robotic systems. They offer the necessary accuracy for intricate movements. Examples include Dynamixel AX-12A and Kollmorgen AKM2G.
- Low-Cost Servo Motors: Low-cost servo motors provide budget-friendly options for applications with basic positioning requirements. Common models include TowerPro MG90S, SG92R and EMAX ES08MAII.
- Waterproof Servo Motors: Waterproof servo motors are designed to resist water ingress, making them suitable for outdoor or marine applications. Examples include Savox SW-1210SG and Traxxas 2085X.
- Metal Gear Servo Motors: Metal gear servo motors feature gears made of metal, providing increased durability and strength. They are suitable for high-stress applications. Noteworthy models are TowerPro MG995, Hitec HS-7950TH and Futaba S9373SV.
What is a servo motor used for?
How does a servo motor work?
Servo motors operate based on feedback control. They receive electrical signals (pulses) that determine the desired position, and an internal sensor (usually a potentiometer) constantly sends feedback to ensure the motor reaches and maintains the specified position accurately.
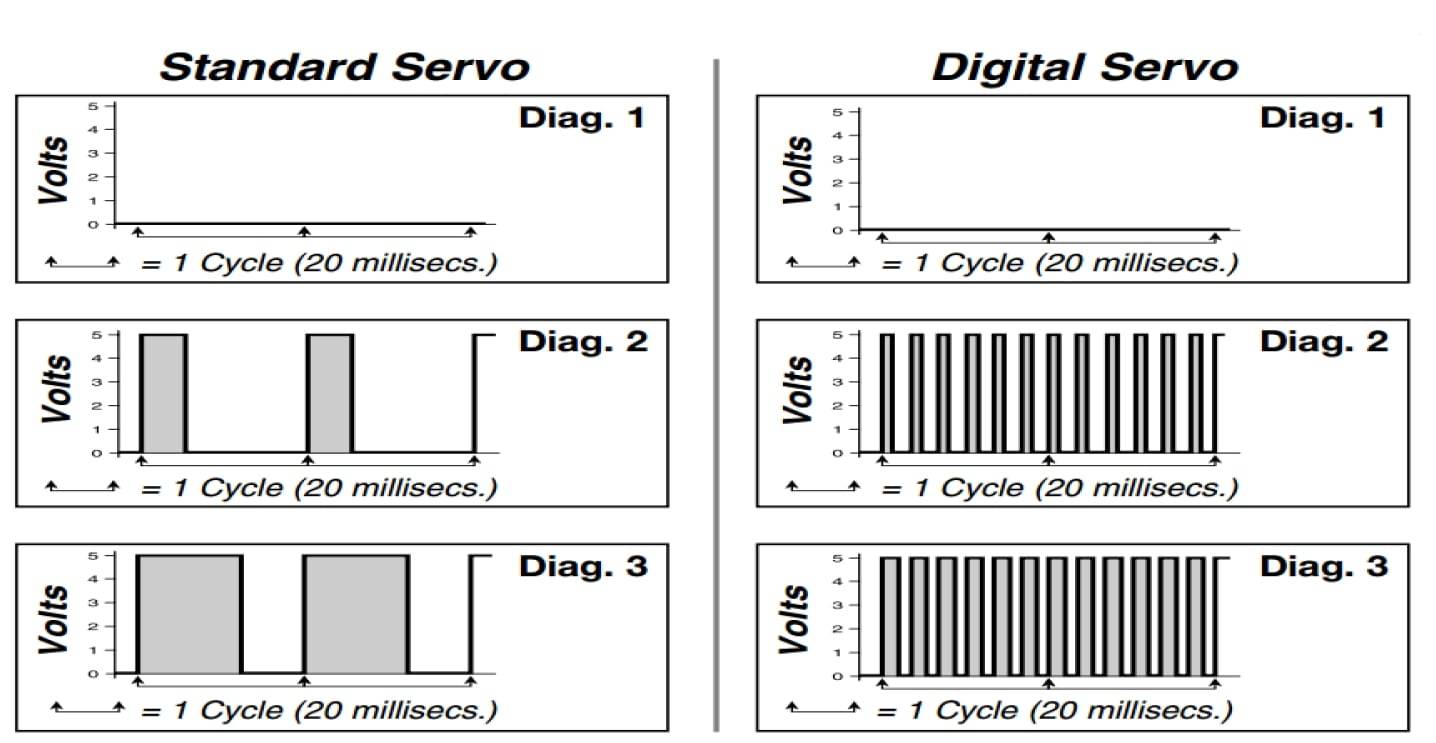
What is the difference between an analog and a digital servo motor?
Analog (Standard) servo motors use analog signals for control, while digital servos operate on digital signals. Digital servos offer higher precision, faster response times, and enhanced accuracy compared to their analog counterparts.
Can I use any servo motor with Arduino?
Yes, Arduino is compatible with most standard servo motors. Arduino boards generate the necessary control signals, typically in the form of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), making them suitable for driving servo motors in various projects.
What is the significance of torque in a servo motor?
Torque in a servo motor is crucial as it determines the motor's ability to rotate an object. Higher torque enables the motor to move heavier loads, making it an important consideration when selecting a servo for specific applications.
How to control the speed of a servo motor?
Servo motors can be controlled by adjusting the pulse width of the input signal. A wider pulse generally results in a higher speed. However, the specific method might vary based on the servo model and the control system used.
Can a servo motor rotate continuously?
While standard servo motors have a limited range of rotation, continuous rotation servos are designed to rotate indefinitely. They are often used in applications where continuous movement is required, such as in robotics and conveyor systems.
How to power a servo motor?
Servo motors are powered using a direct current (DC) power source. The voltage and current requirements vary by servo model, so it's essential to provide the specified power to ensure proper operation.
Can I modify the rotation range of a servo motor?
It is not easy and we do not advise you to do so but if you insist on doing it, yes, it is possible to modify the rotation range of a servo motor. This can be achieved by adjusting the mechanical stops or using additional hardware to limit the movement within a specific range.
What is the difference between a servo motor and a stepper motor?
While both are used for precise control, the main difference lies in their operation. Servo motors use feedback for precise positioning, while stepper motors move in fixed steps, making them suitable for different applications based on the required precision.
Can a servo motor be used for precise positioning?
Yes, servo motors excel at precise positioning due to their closed-loop control system. The feedback mechanism ensures accurate and controlled movement, making them ideal for applications requiring precision.










