Product added to cart
Yes, the module is fully compatible with Arduino boards. It can be easily connected and programmed using Arduino IDE.
Creating an account has many benefits: check out faster, keep more than one address, track orders and more.

We offer free shipping on all orders over $35 and under 2kg.
Please note that free shipping is only available for orders under 2kg.
DHL is a renowned shipping courier known for its global reach and reliable delivery services. With a vast network and advanced logistics capabilities, DHL offers fast and secure shipping solutions for international shipments.
For the majority of countries, DHL provides an estimated delivery time of 5 to 7 days.
In certain instances, DHL may not be available for shipments to EU countries. In such cases, we may opt to ship your order using FedEx instead of DHL. Rest assured, FedEx offers a comparable estimated time of arrival (ETA) and your package should typically arrive within 5-7 days.
The base shipping cost for DHL is $35. You can see the final shipping amount on the checkout page. If your order is over $200 and less than 2kg, you will qualify for free shipping through DHL Express.
Yun Express is a shipping courier known for its reliable and efficient international shipping services. With a strong global network and advanced logistics solutions, Yun Express ensures timely delivery and provides tracking options for customers to monitor their shipments.
The delivery time in most cases is 10-15 business days. If your order is over $35 and less than 2kg,you will qualify for free shipping through YunExpress.
YunExpress shipments can be tracked here: https://www.yuntrack.com/
Our shipping term is FOB Shenzhen, which does not cover any customs fees. It is important to note that you may be responsible for paying any charges imposed by your country's government, such as duties, taxes, and additional fees imposed by the courier company.
 YwRobot Rotary Potentiometer Analog Knob Module Previous
YwRobot Rotary Potentiometer Analog Knob Module Previous 
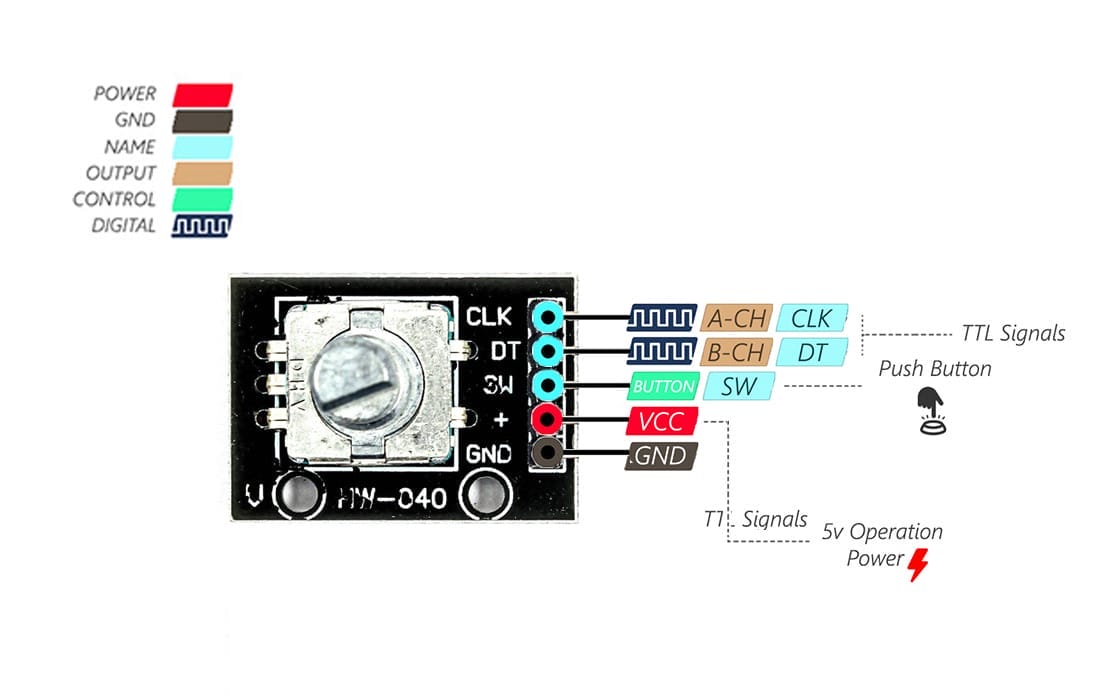
The KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module with Push Switch is a versatile electronic component designed for precise rotary motion and push-button functionality. It's commonly used in a variety of projects including DIY electronics, robotics, 3D printers, and more. This module combines a rotary encoder with a push switch, offering users a compact and efficient input solution for their projects.
Key features of KY-040 Rotary Encoder Module with Push Switch
Avoid applying excessive force when rotating the encoder or pressing the push button to prevent damage to the module.
The main differences between brush encoders like the KY-040 and optical encoders like the HN3806 lie in their working principles, construction, accuracy, and environmental robustness:
In summary, while both brush encoders like the KY-040 and optical encoders like the HN3806 serve similar purposes of providing position feedback, they differ significantly in their working principles, construction, accuracy, and environmental robustness. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
You can see more encoders on this link.
Yes, the module is fully compatible with Arduino boards. It can be easily connected and programmed using Arduino IDE.
The push switch allows users to trigger actions or events within their projects with a simple press, adding versatility to the module's functionality.
The rotary encoder provides high precision feedback, typically with a resolution of 20 pulses per revolution, enabling accurate measurement of rotational movement.
While the module is primarily designed for hobbyist and DIY projects, its durable construction and reliable performance make it suitable for certain light-duty industrial applications.
While both brush encoders and optical encoders serve similar functions of providing position feedback, optical encoders generally offer greater durability due to their non-contact operation, resistance to environmental factors, and lower maintenance requirements. Brush encoders may still be suitable for certain applications but may require more frequent maintenance and have a shorter lifespan compared to optical encoders.
helloxxxx

Please complete your information below to login.
Sign In
Create New Account