Specifications of NRF24L01 Wireless RF Transceiver Module (2.4GHz):
- Chipset: NRF24L01
- Operating Frequency: 2.4GHz ISM band
- Modulation: GFSK (Gaussian Frequency Shift Keying)
- Communication Protocol: Enhanced ShockBurst (ESB) for easy point-to-point communication
- Operating Voltage: 1.9~3.6V recommended 3.3V (5V tolerant I/O pins) (dont use Arduino 3.3v pin for power it up)
- Communication Range: Varies depending on power settings and environmental factors, but can typically reach up to 100 meters in open space.
- Data Rate: Adjustable data rates, commonly used rates include 250kbps, 1Mbps, and 2Mbps.
- DIP-8 ultra small package, built-in 2.4G antenna
- Supports six channels of data reception
- Supports general modulation methods such as GFSK/FSK
- Average emission current as low as 110mA
- Average emission current as low as 110mA
- Receive sensitivity: -96dBm@250kbps
- Maximum transmit power: +7dBm
- 4-wire SPI interface with speeds up to 10MHz
- Internal integrated intelligent ARQ baseband protocol engine
- Transceiver data hardware interrupt output
- Support 1bit RSSI output
- Output Power: Adjustable power levels for different communication ranges.
- Interface: SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) for communication with microcontrollers or other devices.
- Operating Temperature Range: -20°C to +70°C.
- Size: 15x28mm.
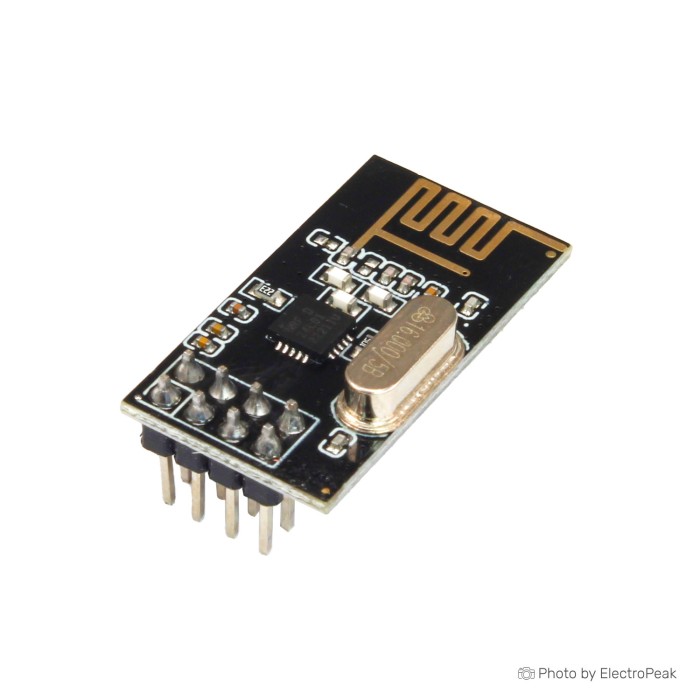
Pinouts of nRF24L01 transceiver module
The NRF24L01 module has 8 pins as you can see in the picture below.

- VIN: module power supply (1.9 to 3.9 volts)
- GND: Ground
- MOSI: Data transmission line for SPI protocol
- MISO: Data receiving line for SPI protocol
- SCK: Synchronization for SPI protocol
- IRQ: Interrupt for SPI protocol
- CSN: Module selection for SPI protocol (reverse)
- CE: SPI protocol activation
Use Cases of nRF24L01 transceiver modules:
The nRF24L01 transceiver module is versatile and finds application in various projects that require wireless communication in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Here are some common use cases:
- Wireless Sensor Networks: nRF24L01 modules are popular in creating wireless sensor networks where sensor nodes communicate data to a central hub. This is commonly used in home automation, environmental monitoring, and industrial applications.
- Remote Control Systems: Building remote control systems for devices like robots, drones, or home appliances. The modules allow for simple and reliable communication between the remote control unit and the controlled device.

- IoT (Internet of Things) Projects: Integrating nRF24L01 modules into IoT projects where low-power, short-range communication is required. This can include smart home devices, wearable technology, and other IoT applications.
- Wireless Data Logging: Creating wireless data logging systems for monitoring and logging data from remote locations. This is useful in agriculture, weather stations, and environmental research.
- Toy and Hobbyist Projects: Implementing wireless communication in toy projects or hobbyist applications. For example, creating a wireless-controlled car, quadcopter, or other remote-controlled devices.
- Mesh Networking: Establishing mesh networks where multiple nodes communicate with each other to relay data. This is beneficial in scenarios where a centralized communication point is impractical or when redundancy and robustness are crucial.

- Home Automation: Integrating nRF24L01 modules into home automation systems to wirelessly control and monitor smart devices such as lights, thermostats, and security systems.
- Robotics: Integrating the modules into robotics projects for wireless communication between different components of a robot, enabling remote control or data exchange between sensors and controllers.
Usage tips of nRF24L01 transceiver modules:
Using the nRF24L01 transceiver module effectively requires attention to various aspects of configuration, power management, and interference mitigation. Here are some usage tips to help you get the most out of the nRF24L01 module:
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power supply within the recommended voltage range (1.9V to 3.6V) to prevent erratic behavior and maximize the module's performance.
- Consider adding capacitors near the power pins to stabilize the voltage and reduce noise.
- Antenna Configuration: Choose an appropriate antenna based on your application and required range. Antenna options include PCB trace antennas or external antennas.
- Position the antenna away from obstacles and metal surfaces to minimize signal reflection and interference.
- External Components: Include decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to stabilize the voltage and reduce noise.
- If needed, add a low-pass filter to the power supply to minimize high-frequency noise.
- Grounding: Pay attention to proper grounding to minimize noise and interference. Connect the ground pins of the module to a common ground reference in your circuit.
- Consideration for Interference: Be aware of potential interference from other devices operating in the 2.4 GHz band, such as Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and microwave ovens.
By following these usage tips, you can enhance the reliability and performance of the nRF24L01 transceiver module in your wireless communication projects.
What is the effective range of the NRF24L01 radio module without using an external antenna?
The transmission range of the nRF24L01 module without an external antenna can vary based on several factors, including the power level, environmental conditions, and potential obstacles. Generally, without an external antenna, the range is limited compared to modules with external antennas.
Here are some rough estimates for the transmission range of the nRF24L01 module without an external antenna:
- Indoor Range: In an indoor environment with walls and obstacles, the range may typically be around 20 to 30 meters (65 to 100 feet). However, this can vary based on the building materials and other sources of interference.
- Outdoor Range: In an open outdoor environment with minimal obstructions, the range might extend to around 50 meters (165 feet) or more. The absence of walls and obstacles allows for better signal propagation.
It's important to note that these are general estimates, and the actual range can be influenced by factors such as:
- Power Level: The transmission power level of the nRF24L01 module can be adjusted. Higher power levels can extend the range but may also increase power consumption.
- Interference: The 2.4 GHz frequency band, used by the nRF24L01, is shared with various other devices like Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and microwave ovens. Interference from these devices can impact the effective range.
- Antenna Type: If you are using a module variant with an integrated PCB trace antenna, the range may be different than those with external antennas. External antennas generally provide better performance.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as humidity, temperature, and electromagnetic interference in the environment can influence the signal propagation.
For applications where an extended range is required, or in environments with obstacles and interference, adding an external antenna to the nRF24L01 module is a common practice. An external antenna can significantly improve the module's range and overall performance. When using an external antenna, it's essential to consider proper matching and impedance matching for optimal results.
How do I interface a nRF24L01 transceiver modules with a microcontroller?
Interfacing an nRF24L01 transceiver module with a microcontroller involves connecting the module to the microcontroller's GPIO pins and configuring the microcontroller to communicate with the module using the SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) protocol.
Components Needed:
- nRF24L01 transceiver module
- Microcontroller (e.g., Arduino, ESP32, STM32, etc.)
- Power supply for the nRF24L01 (within the specified voltage range)
If you are using development boards that uses 5v as a power supply voltage, you can use 5 to 3.3v DC/DC converter module to supply the power of nRF24L01 modules.
You can read how to €œEstablishing a Wireless Connection with Arduino and NRF24l01€ and €œInterfacing NRF24L01 Wireless Transceiver Module with Arduino€ for more information.
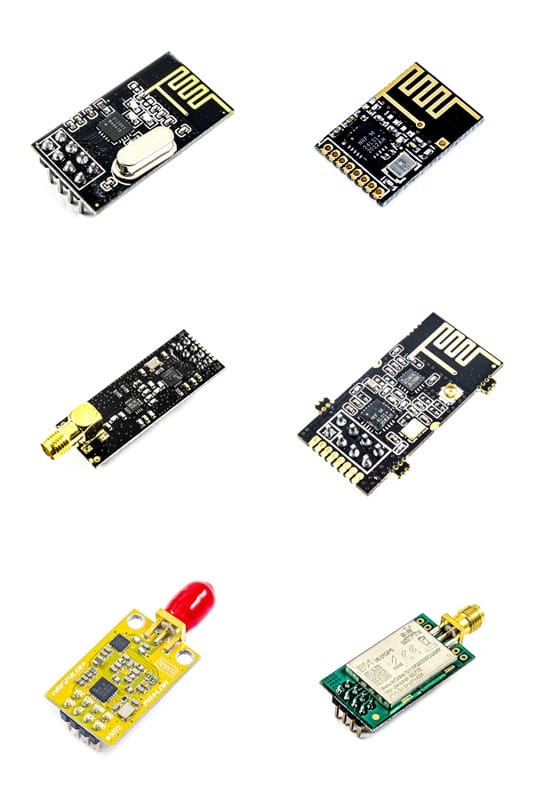
Comparison of different nRF24 modules
Before purchasing an nRF24 module, it is better to understand the differences between nRF24 modules available in the market. In this section, we introduce the major differences between different types of nRF24 modules, so that you can choose the right module based on your needs.
Power Amplification (PA) and Low Noise Amplification (LNA) capabilities: Some modules have Power Amplification (PA) and Low Noise Amplification (LNA) features that can increase the communication range. These modules are often labeled as "nRF24L01+PA+LNA". You can see one of these modules through this link.
The possibility of installing an external antenna: Different modules may have different antenna configurations. Some modules have an internal antenna, while others have an external antenna connection to increase range. You can see one of these modules through this link.
Voltage range: The working voltage range can be different among modules. Although most modules work in the 3.3 V range, it is necessary to pay attention to this parameter when choosing a module.
Data rate: The maximum data rate supported by the nRF24 module can vary. While the standard data rate is 250 kbps, some modules may support higher rates such as 1 Mbps or 2 Mbps.
Effective range: The effective range of communication can vary based on factors such as the presence of PA/LNA, antenna type, and environmental conditions. Some modules may have more range than others.
Cost: The cost of nRF24 modules can vary based on features and specifications. Modules with more features, such as external antennas or PA/LNA, may be more expensive than other modules.
Manufacturer and Brand: Various manufacturers produce nRF24 modules. The quality of the parts used in them is different and causes a change in the quality of sending and receiving data.
In the image below, you can see the types of modules available.

FAQs
What is the range of the nRF24L01 module?
The effective range of the nRF24L01 module is influenced by factors like power supply voltage, antenna design, and environmental conditions. Typically, it can achieve reliable communication within a range of 20 to 100 meters.
Can I use multiple nRF24L01 modules in the same area?
Yes, the nRF24L01 modules support the use of multiple channels, allowing you to use multiple modules in the same vicinity without interference. You can configure each module to operate on a different channel.
What is the role of the antenna in the nRF24L01 module?
Can I use the nRF24L01 module for battery-powered devices?









Please complete your information below to login.
Sign In
Create New Account