Product added to cart
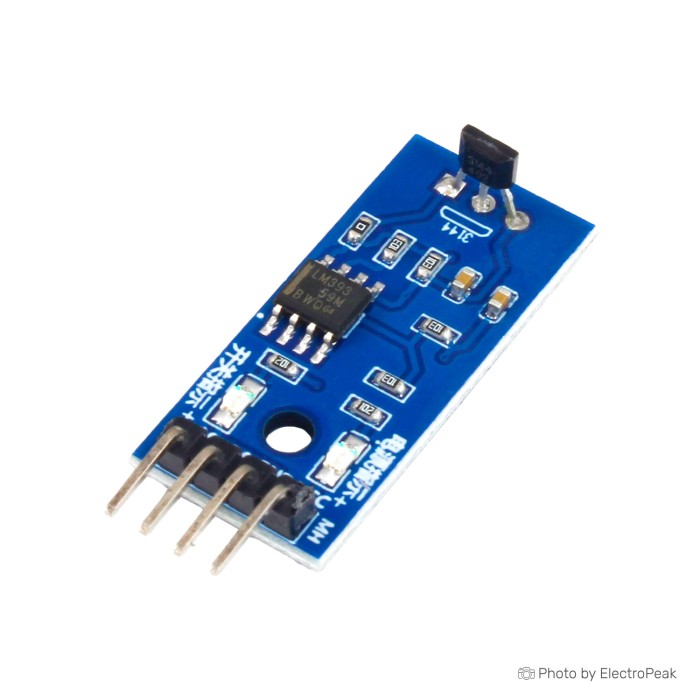
44E Hall Effect Sensor Module
$0.2400
In stock
SKU
SEN-09-010
Volume discounts:
- +100 4 % $0.2310
- +500 6 % $0.2260
- +1000 8 % $0.2220
- +5000 10 % $0.2170
- +10000 11 % $0.2130
Ships in 2-3 business days, then:
Free delivery in10-15 days by YunExpress on orders over $35.
Free delivery in5-7 days by DHL on orders over $200.
More shipping info
Shop with confidence Learn More
 Reed Switch Magnet Sensor Module Previous
Reed Switch Magnet Sensor Module Previous 
The 44E Hall Effect Sensor Module is designed to detect the presence of a magnetic field and convert it into an electrical signal. It employs a 44E Hall Effect sensor, which is a small, versatile linear Hall-effect device that is operated by the magnetic field from a permanent magnet or an electromagnet. These modules are versatile and find applications in various fields, including electronics, automation, and robotics.
The Hall Effect sensor works on the principle that when exposed to a magnetic field, it produces a voltage that is proportional to the strength and polarity of the field. The 44E Hall Effect Sensor Module typically provides either a digital (TTL) or analog voltage output depending on the module variant. In digital mode, the output is either high or low to indicate the presence or absence of a magnetic field, while in analog mode, the output voltage varies with the strength of the field. It sensitive to both North and South magnetic poles.
Specifications of 44E Hall Effect Sensor module:
- Sensor Type: 44E Hall Effect sensor
- Measuring magnetic field range: min:±650, typ: ±1000
- Output Signal: Digital (TTL. Max 15mA) or Analog (voltage) (depends on the supply voltage and varies in proportion to the strength of the magnetic field)
- Analog output voltage span:0 to Vcc-1.0
- Analog Quiescent Output Voltage:5v (at Vcc = 5.0)
- Supply Voltage: Typically 3.3V to 6V DC
- Sensitivity: 6mV/gauss
- Operating temperature: -40„ to 85„
- Fixing: A Fixing bolt hole for easy installation
- Dimensions: 38x14 mm
Use Cases of 44E Hall Effect Sensor modules:
Hall Effect Sensor modules are versatile components that can be employed in various applications due to their ability to detect changes in magnetic fields. Here are some common use cases for 44E Hall Effect Sensor modules:
- Proximity Detection: Hall Effect Sensors such as 44E can be used for proximity sensing applications. For example, they can detect the presence of a magnet, allowing for non-contact proximity switches in industrial settings.
- Position Sensing: By attaching a magnet to a moving object, Hall Effect Sensors can be utilized to determine the position of the object. This is commonly applied in applications like rotary encoders and linear position sensors.
- Speed Measurement: Hall Effect Sensors can be used to measure the speed of a rotating object with the help of magnets attached to the rotating element. This is applicable in scenarios such as motor speed control.
- Current Sensing: Hall Effect Sensors can be integrated into current sensors for measuring the flow of electric current. This is particularly useful in applications like motor control and power monitoring.
- Magnetic Switches: Hall Effect Sensors are often employed in magnetic switches. When a magnet is brought close to the sensor, it triggers a change in the sensor's output, allowing for the creation of simple and reliable switch mechanisms.
- Brushless DC Motor Control: In conjunction with magnets on the rotor, Hall Effect Sensors can be employed for commutation in brushless DC motors. This enables precise control of the motor's speed and direction.
- Pulse Counting: Hall Effect Sensors can be used to count the number of revolutions or rotations in various devices, providing a pulse output for each rotation.
- Fluid Level Sensing: By attaching a magnet to a float, Hall Effect Sensors can be employed for fluid level sensing in tanks and containers.
Usage tips of 44E Hall Effect Sensor module:
- Magnetic Field Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the magnetic field with the sensor. The sensor's response is influenced by the orientation and strength of the magnetic field, so consider the positioning of magnets or magnetic sources.
- Avoid Magnetic Interference: Be mindful of potential sources of magnetic interference in the vicinity of the sensor. Other magnets, electronic devices, and ferrous materials can affect sensor readings. Position the sensor away from sources of interference.
- Implement Magnetic Shielding: If magnetic interference is a concern, consider using magnetic shielding materials to protect the sensor. This is particularly important in applications where external magnetic fields can impact sensor accuracy.
- Calibrate the Sensor (if required): Depending on the application, you may need to calibrate the Hall Effect Sensor to ensure accurate readings. Calibration may involve adjusting threshold levels, sensitivity, or scaling the output to match the desired range.
- Check for Output Stability: Monitor the stability of the sensor output over time. If you notice drift or instability, investigate potential causes such as changes in temperature or aging of components.
How do I interface a 44E Hall Effect Sensor with a microcontroller?
Hall Effect Sensors can be interfaced with a microcontroller using the sensor's output signal. Analog sensors can be connected to an analog input pin, while digital sensors can be connected to a digital input pin.
Our suggestion for new users is to use Arduino boards. For example, you can use Arduino UNO board.
Write Your Own Review




Please complete your information below to login.
Sign In
Create New Account