PN532 NFC RFID Module Features
If you are experienced in electronics, you have probably heard of RFID (radio-frequency-identification) and NFC (near-field-communication). PN532 module is a kind of RFID-NFC module that uses I2C, SPI and HSU protocols for communication. This module is based on NXP PN532 IC. The key features are:
- Support I2C, SPI, high-speed UART (HSU) protocols
- PCB design for antenna
- Communication distance: 5 to 7cm
- RFID reader and writer supports the following:
- Mifare 1K 4K, Ultralight and DesFire cards
- ISO / IEC 14443-4 cards such as CD97BX, CD light, DesFire and P5CN072 (SMX)
- Innovision Jewel cards such as the IRT5001 card
- FeliCa cards such as RCS_860 and RCS_854
You can download the datasheet of this module here.
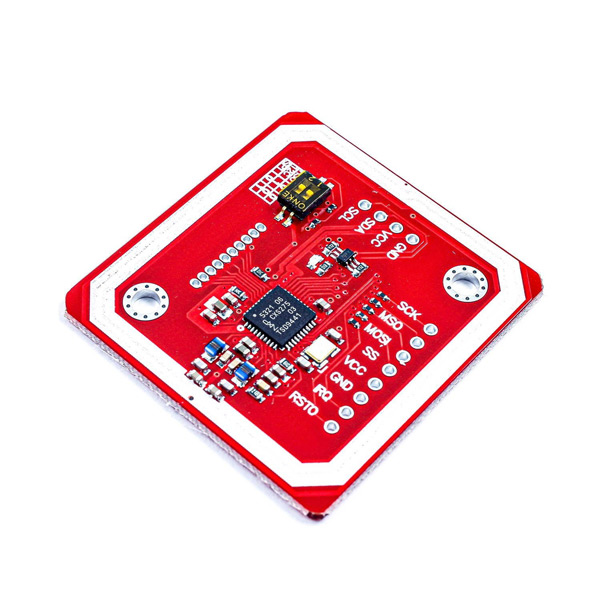
PN532 NFC RFID Module Pinout
As mentioned above, this module supports HSU, SPI and I2C communication protocols. The module uses separate pins for SPI protocol, but the pins used for I2C and HSU communication protocols are the same. The names of the I2C pins are on the front of the module and the names of the HSU pins are on the back of the module. HSU is the default protocol of the module. You can change the communication protocol of the module to one of the I2C, SPI or HSU using DIP switches on the module.
This Module has 16 pins. The pins of each protocol are as follows:
I2C protocol:
- VCC: Module power supply – 5V
- GND: Ground
- SDA: Data pin
- SCL: Clock pin
SPI protocol:
- VCC: Module power supply – 3-5V
- GND: Ground
- SCK: Clock pin
- MISO: Output data pin
- MOSI: Input data pin
- SS: Slave select
- IRQ: Interrupt pin
- RSTO: Reset pin
HSU protocol:
- VCC: Module power supply – 5V
- GND: Ground
- TXD: Transmit data pin
- RXD: Receive data pin
You can see the pinout of this module in the image below.
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Interfacing PN532 NFC RFID Module with Arduino
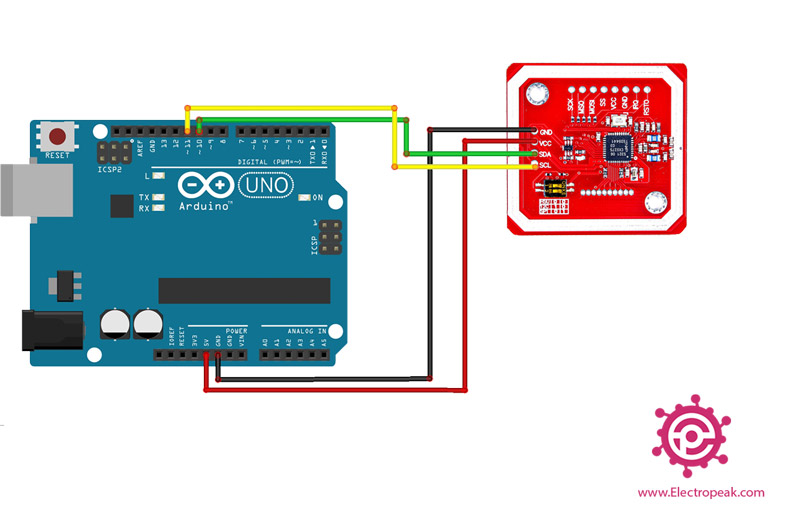
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit show how you should connect Arduino to PN532 module. Connect wires accordingly.
Step 2: Library
Note
If you need more help with installing a library on Arduino, read this tutorial: How to Install an Arduino Library
Step 3: Code
Upload the following code to Arduino. After that open the Serial Monitor.
/*
PN532-NFC-RFID-Module-Library
modified on 18 Nov 2020
by Amir Mohammad Shojaee @ Electropeak
Home
based on www.electroschematics.com Arduino Examples
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <PN532_SWHSU.h>
#include <PN532.h>
SoftwareSerial SWSerial( 10, 11 ); // RX, TX
PN532_SWHSU pn532swhsu( SWSerial );
PN532 nfc( pn532swhsu );
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Hello Maker!");
nfc.begin();
uint32_t versiondata = nfc.getFirmwareVersion();
if (! versiondata) {
Serial.print("Didn't Find PN53x Module");
while (1); // Halt
}
// Got valid data, print it out!
Serial.print("Found chip PN5"); Serial.println((versiondata>>24) & 0xFF, HEX);
Serial.print("Firmware ver. "); Serial.print((versiondata>>16) & 0xFF, DEC);
Serial.print('.'); Serial.println((versiondata>>8) & 0xFF, DEC);
// Configure board to read RFID tags
nfc.SAMConfig();
Serial.println("Waiting for an ISO14443A Card ...");
}
void loop(void) {
boolean success;
uint8_t uid[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Buffer to store the returned UID
uint8_t uidLength; // Length of the UID (4 or 7 bytes depending on ISO14443A card type)
success = nfc.readPassiveTargetID(PN532_MIFARE_ISO14443A, &uid[0], &uidLength);
if (success) {
Serial.println("Found A Card!");
Serial.print("UID Length: ");Serial.print(uidLength, DEC);Serial.println(" bytes");
Serial.print("UID Value: ");
for (uint8_t i=0; i < uidLength; i++)
{
Serial.print(" 0x");Serial.print(uid[i], HEX);
}
Serial.println("");
// 2 second halt
delay(2000);
}
else
{
// PN532 probably timed out waiting for a card
Serial.println("Timed out! Waiting for a card...");
}
}
The required libraries must be included first. This code is for HSU mode. Next, 2 pins 10 and 11 are defined as serial pins in order to connect to the module. If we bring the card near to the module, it is detected and its data appears on Serial Monitor.
See the image below. Hold the card close to the module and then take it away. As you see, first the card is detected and then its data is displayed on Serial Monitor.



Comments (9)
Hello,
is it possible to send sensor info using NFC from Arduino to mobile phone (to open web page)?
I didn’t see anything like this..only the simple open close door etc.
thank you in advance,
Ran
Hi,
No, you cannot use NFC modules to send information. They can only detect NFC cards and send the ID of the detected card to a microcontroller like an Arduino. If you want to send sensor info from Arduino to mobile, you need to use a Bluetooth module like HC-05. You can see the following tutorial for more details on you can use this module:
https://electropeak.com/learn/interfacing-hc-05-bluetooth-wireless-module-with-arduino/
Also for the android App, you can use “Serial Monitor Terminal”.
Hi. I am just trying to test this board on a Arduino Uno. I have copied the code above and paste in Arduino IDE. But something seems to bee wrong. When I compile the program I get the message:
Error compiling for board Arduino Uno.
I have tried to find what’s wrong, but don’t find it. Please, can you help mee?
Hi.
It’s probably because the libraries are not properly installed. The “Library” section of the tutorial is now updated. Try the new libraries to see if it solves the issue.
I have a doubt: the power supply is 5V but on datasheet there is written the max voltage on I2C/SPI pins is PVDD and the max voltage on PVDD is 3.6V, so PN532 has 5V tollerant pins?
arduino ide stops with
Arduino: 1.8.19 (Windows 7), Board: “ESP32 Wrover Module, Minimal SPIFFS (1.9MB APP with OTA/190KB SPIFFS), QIO, 80MHz, 921600, None”
Alternatives for SoftwareSerial.h: []
ResolveLibrary(SoftwareSerial.h)
-> candidates: []
testing_hsu:10:28: fatal error: SoftwareSerial.h: No such file or directory
compilation terminated.
I guess i dont have that library, and the guide doesnt say to add it, i know its common and i can add it, but thats a missing step…..
(was tested on a fresh install)
Hi.
The code is only written for Arduino AVR Boards and you can’t use it for other boards like ESP32.
Is communication between two RFID modules possible? I was thinking about using one as a recorder and the other as a receiver, the reason for this idea is a way to see how bus pass chargers work, if it is possible to read the code on these RFID chargers, in other words, I would need read from another device in recording mode.
Hi Anthony,
To my knowledge, it’s not possible to use two RFID readers as both a reader and a writer simultaneously.
Additionally, this model operates within a distance of 1 to 4 cm.
If you need to read something in passing, you might want to consider using a QR-Code scanner with a camera, such as the ESP-CAM