If you’re looking to interface the INA219 current sensor module with an Arduino, you’ve come to the right place. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the necessary steps to get your setup up and running smoothly.
INA219 Current Sensor Module Features
The INA219 module is used to measure both current and voltage at the same time. This module uses I2C communication to transfer the voltage and current data.
Other features:
- Measurement accuracy: 1%
- Maximum measured voltage: 26V
- Maximum measured current: 3.2A.
Note
Pay attention to inductive loads switching. Its instantaneous voltages may damage the circuit.
Download the Datasheet of this sensor here.
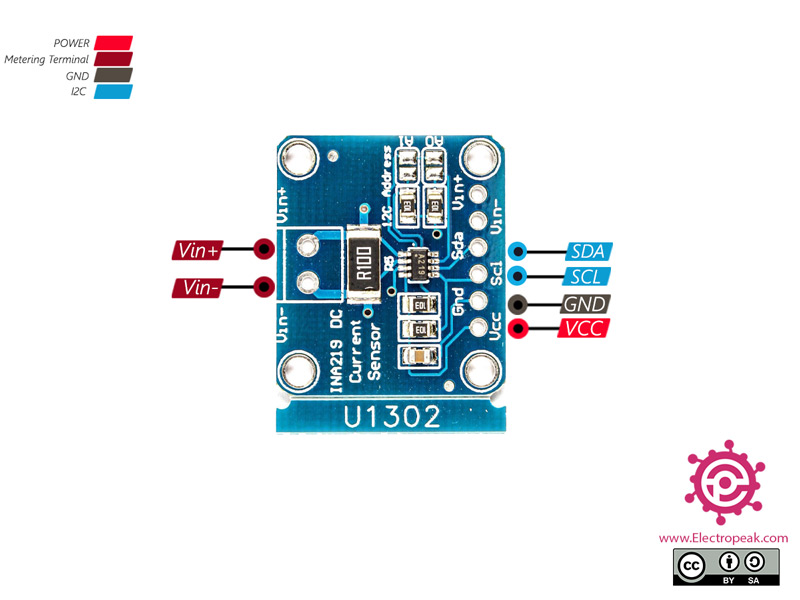
INA219 Current Sensor Module Pinout
This Module has 6 pins:
- VCC: Module power supply
- GND: Ground
- SDA: I2C Data
- SCL: I2C Clock
- Vin-: Load terminal pin
- Vin+: Source terminal pin
You can see the pinout of this module in the image below.
Required Material
Hardware component
Software Apps
Note
Apart from the components above, you also need an LED and a 220ohm resistor for this tutorial.
Step-by-Step Guide to Interfacing INA219 Current Sensor Module with Arduino
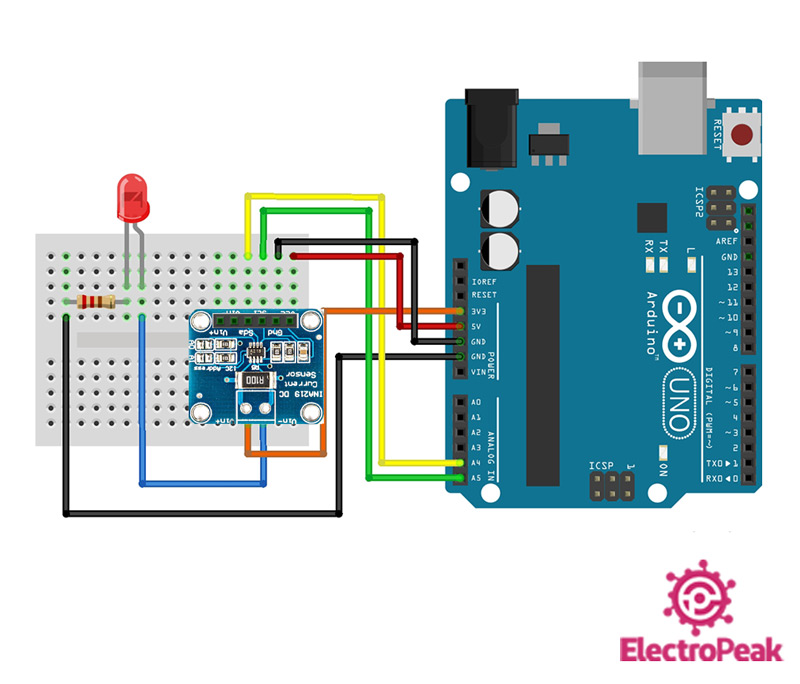
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit shows how you should connect Arduino to INA219 sensor. Connect wires accordingly.
Note
The orange wire (3.3 volts) is called the Bus voltage and the blue wire is called the Load voltage.
Shunt voltage is the potential difference between the Load voltage and the Bus voltage.
Step 2: Library
Go to Library manager, search for INA219 and install the Adafruit INA219 library.
Note
If you need more help with installing a library on Arduino, read this tutorial: How to Install an Arduino Library
Step 3: Code
Upload the following code to Arduino.
/*
DC-Current-Voltage-Sensor-Module
made on 06 Feb 2021
Home
based on Adafruit Example
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_INA219.h>
Adafruit_INA219 ina219;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial) {
// will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
delay(1);
}
uint32_t currentFrequency;
Serial.println("Hello!");
if (! ina219.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find INA219 chip");
while (1) { delay(10); }
}
Serial.println("Measuring voltage and current with INA219 ...");
}
void loop(void)
{
float shuntvoltage = 0;
float busvoltage = 0;
float current_mA = 0;
float loadvoltage = 0;
float power_mW = 0;
shuntvoltage = ina219.getShuntVoltage_mV();
busvoltage = ina219.getBusVoltage_V();
current_mA = ina219.getCurrent_mA();
power_mW = ina219.getPower_mW();
loadvoltage = busvoltage + (shuntvoltage / 1000);
Serial.print("Bus Voltage: "); Serial.print(busvoltage); Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Shunt Voltage: "); Serial.print(shuntvoltage); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Load Voltage: "); Serial.print(loadvoltage); Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Current: "); Serial.print(current_mA); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.print("Power: "); Serial.print(power_mW); Serial.println(" mW");
Serial.println("");
delay(2000);
}
This code is for measuring both voltage and current. We want to find the source voltage and the voltage and current of the load. The source voltage is 3.3V and the load voltage is actually the LED voltage. The current passing through LED is also calculated using the shunt voltage. The shunt resistance creates a very small potential difference called the shunt voltage.
These parameters will be displayed on the Serial Monitor: Bus, Shunt and Load voltage, current and power:
By following these simple steps, you’ll successfully interface the INA219 current sensor module with your Arduino board. Enjoy the accuracy and versatility that the INA219 module brings to your projects!
Remember, if you encounter any issues or require additional support, feel free to reach out. Happy tinkering with the INA219!



Comments (14)
I have followed your instruction to the letter and get the following error message
Failed to find INA219 chip”
Hi.
First check the wiring to make sure all pins are correctly connected to each other. Especially SDA and SCL which must be connected to pins A4 and A5 respectively. If those 2 pins are not properly connected you might get an error like the one you’ve got now. Also, you can use the i2c_scanner in Arduino IDE File -> Examples -> Wire -> i2c_scanner to see if any I2C devices are found. If you still get no I2C scanner, there might be something wrong with the INA219 module itself.
Shouldn’t it be “loadvoltage = busvoltage – (shuntvoltage / 1000)” instead of “loadvoltage = busvoltage + (shuntvoltage / 1000)”?
Hi dear
No,you make mistake
actually the Vbus is Vin- and Vshunt is Vdrop and they sum toghether to get Vload. this is a simple KVL.
please check this address:
https://www.electroniclinic.com/ina219-current-sensor-with-arduino-circuit-and-code-explained/
Dear Sir,
I have followed your step and the voltage can not be shown on serial port monitor.
only current is shown on moinitor.
Hi sir,good day
What exactly is your problem?
you mean dont recevie any measurment or the range is wrong?
Hi,
I am wondering if it is possible to enable a digital output (high) on the Arduino when a specific threshold is reached? this could be used to drive an output and/or act as an alarm.
Do you have any code for this type of function?
Hello sir,
Is it normal that after i followed your steps I got the lines above instead of values ? :
�k������,��^���݊�����xV=���<��d�����i��6|d`<��.��^����,��^���h�Z
h�X��.|�������,#��d�����ݲ�� �Y�i��2|� <�ݪ|��8���a�,+�xT����,��.��^���xT��_�,"��ѡ�,+��t�� �`��*|����� �$+��,��^���ݪ|��8��,��^����.|���xT����,���A�,#�Yt�[���.��^���Yt�[�,"���!�,+�i���|a`��.��^���i��2|� <�x�ZJ(�X �xT� ��,�i��2|`
�h�04����.��^�����`�,+B�h��4<����.|��0���!�,+���!�$+�i��2<�@�x�Z��<��.��^����.��^���i��2|�`
�ݪ|��8�xT����,�Yt�[�,"?� ���i��2|d ��ݺ�� �����!aU�B�xT����,�xV=���<��.|��0�Xt�[�,"��t�� ���x����<��.��^������,#��t�� ����.��^���i��2|�`
��,��^����d�����Xt�[�,"�i���|a`�ݺ�� �Y�xT� ��,�i��2|�`<�h�$
(�X�xT� ��,��xT����,�xT��_�,"�Yt��[��i��6|�
�i��2<�@�ݪ�����i��2|“
�h�$
h�X���a�,+�i��2|d ��xt�[�,"�ݲ�� �Y��.|��A��xt� �<"X �i��2|` <��.��^���xT� ��,���`�,+�h�0<��`��.��^����� �,+�Yt�[��i��2|�
���� ���h��2<�@��.|����.��^���ݪ�����x�$J(X �ݢ|��8�xV= ��<��,��^����ѡ�,+�h�44��`�i��2|` <�ݪ|��8�h�Z
(�X�xV�Z��<�i��6|d`��xT� ��,��ѡaU�B�Yt�[���d�����x���t 6�xV�Z��<�h�Z
h�X?� �Y�i��6|d`<�h�04��`�x�$H(X ���!�,+B����,#�h�0<�`�ݒ�8�xV=���<���!�,+�xV�Z��<�h�Z
Hi sir.
You have got the wrong baud rate. You should adjust it at 115200
Hi Amir
Very appreciate your posting here. I Have a question regarding the serial baudrate. Can we user lower baudrate ie: 9600 ? as im trying to connect the Arduino board to not only INA219 but other board also.
Thanks in advance.
Regards
Hi
To change the baud rate, simply write your desired speed in the line below.
Serial.begin(115200);Which software did you use to draw the circuit diagram in “Step 1: Circuit”? Did the software has INA219 listed in the component list?
Hi Teena
we used the Fritzing software to show the wiring. In addition, INA219 is not in the component list.
If you want to design the PCB, you should use Proteus or Altium.
Hate to say I love it when someone try’s to correct someone and they end up being wrong… Thanks for example super simple logic. Was going to just use a Shunt resistor but with this I can do a little more. Plus get an idea of how fast I can move windows before considering it either shut or obstructed. Wanting to build a Smart module for my car windows for auto up and down but also want to throw on a canbus hat as well so I can control the windows on a touch display / automatically. Along with more easily control other locks and windows with minimal wiring over the canbus.