DRV8833 Dual Motor Driver Features
Today, speed and direction control of DC motors is very important and useful. The H-bridge circuit is one of the most common techniques to control a DC motor. The DRV8833 dual-channel module uses this technique to control two DC motors.
This dual H-bridge motor driver can drive two DC motors, a stepper motor or other inductive loads.
The driver supply voltage is 2.7 to 10.8V and the allowable continuous current is 1.5A and the maximum allowable current is 2A.
Some common applications are:
- POS printers
- Toys
- Robotic
- Office automation systems
Note
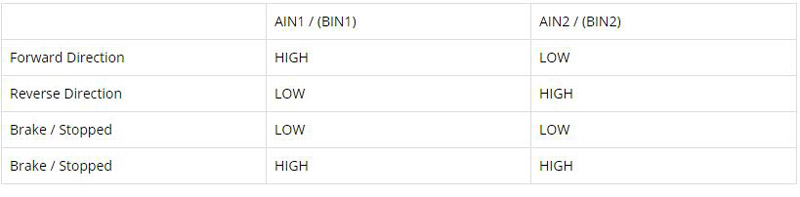
This module has no PWM pin, so the speed of DC motors cannot be precisely controlled and it can only control the direction of DC motors. DC motors can be controlled in either direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise) using two control pins.
You can download the datasheet of this module here.
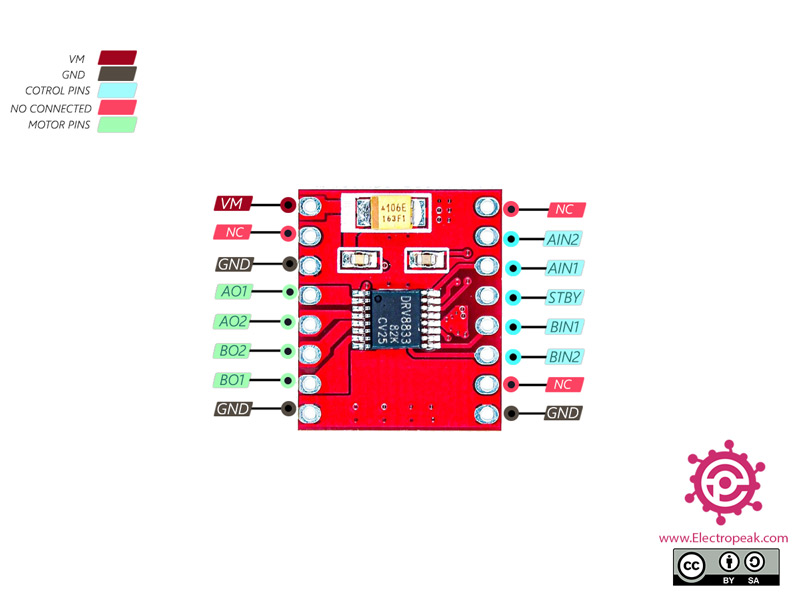
DRV8833 Dual Motor Driver Pinout
This Module has 16 pins:
- VM: Motor voltage
- GND: Ground – three ground connected to each other
- AO1: Positive end for motor A
- AO2: Negative end for motor A
- BO1: Positive end for motor B
- BO2: Negative end for motor B
- AIN1: Control signal for motor A
- AIN2: Control signal for motor A
- BIN1: Control signal for motor B
- BIN2: Control signal for motor B
- STBY: To active Standby mode, it should be HIGH
- NC: Not used
You can see the pinout of this module in the image below.
Note: Different modes of the control signals provide different performance modes for DC motors. The table below shows the different modes.
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Interfacing DRV8833 Dual Motor Driver Module with Arduino
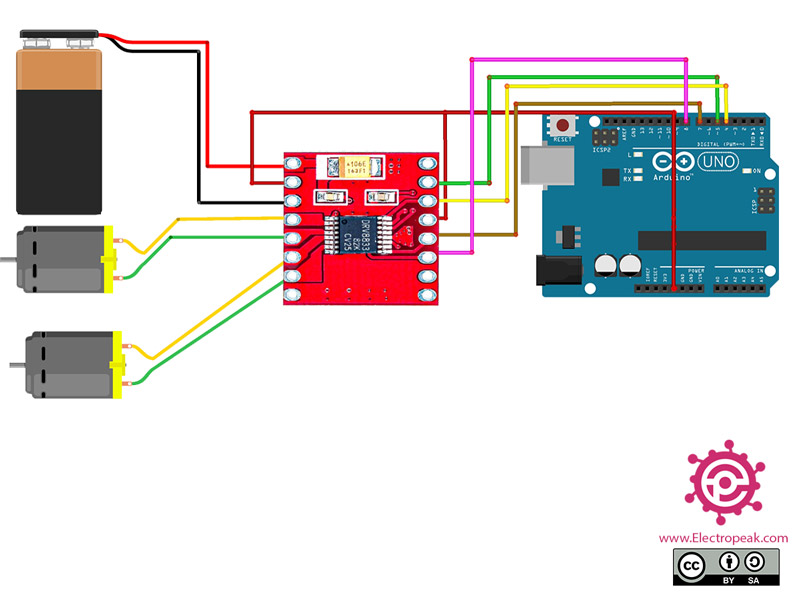
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit show how you should connect Arduino to DRV8833 module. Connect wires accordingly.
Note
Connect STBY pin to VCC pin.
Warning
Be careful not to use power supply greater than 6V, because the motor maximum safe voltage is 6V.
Step 2: Code
Upload the following code to your Arduino.
/*
DRV8833-Dual-Motor-Driver-Module
made on 23 Nov 2020
by Amir Mohammad Shojaee @ Electropeak
Home
*/
#define AIN1 4
#define AIN2 5
#define BIN1 7
#define BIN2 8
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(AIN1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN2,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(AIN1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(BIN2,LOW);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(AIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN2,LOW);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(AIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2,HIGH);
digitalWrite(BIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN2,HIGH);
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(AIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN2,LOW);
delay(1000);
}
This code is for controlling two DC motors simultaneously. First, motors rotate clockwise. Then stop for 1 second, after that they rotate counter-clockwise. Then the motors stop again for 1 second, and the same happens.

Comments (6)
1. How to connect to Nema 17 to DRV8833 ?
2. What is stepping sequence ?
Hi Peter,
to connect Nema17 to DRV8833, u should use this wiring.
And this one for code
#include
// change this to the number of steps on your motor
#define STEPS 200
// create an instance of the stepper class, specifying
// the number of steps of the motor and the pins it's
// attached to
Stepper stepper(STEPS, 4, 5, 6, 7);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Stepper test!");
// set the speed of the motor to 30 RPMs
stepper.setSpeed(60);
}
void loop()
{
Serial.println("Forward");
stepper.step(STEPS);
Serial.println("Backward");
stepper.step(-STEPS);
}
1. Is it possible to add an rf module (nrf240lL01) to make an RC?
“Hi Arhi,
Certainly, you can!
NRF24 provides wireless communication, enabling you to transmit RC data.
If you’re interested in using your phone as a remote control for your RC, consider the ESP32.(no need use an Arduino) and handle every thing.
How do you connect the same DRV8833 modul with N20 motors and Uno R3 arduino to make a line follower robot? any way since i tried the same but it doesnt seem to work
Hello,
DRV8833 serves as a motor driver, while N20 is a compact motor. To create a line follower, incorporate IR sensors to detect the line, utilize an Arduino to interpret this data, and send commands to the motor driver to control movement.
you can read this links too. link1 link2