NEO-7M GPS Module Features
GY-NEO-7M module is an advanced GPS module that supports UART communication protocol with active antenna. You can interface this module easily with any microcontroller. This module has a rechargeable battery and can also be connected directly to a computer using a USB to TTL converter.
This module can receive data and then calculate the geographical position with a very high accuracy and speed. In addition to supporting BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, GPS / QZSS, the module has internal memory to save settings. This module is compatible with Arduino and can be used in any project.
Tip
The on-board LED starts blinking when module is connecting to GPS satellites.
You can download the datasheet of this module here.
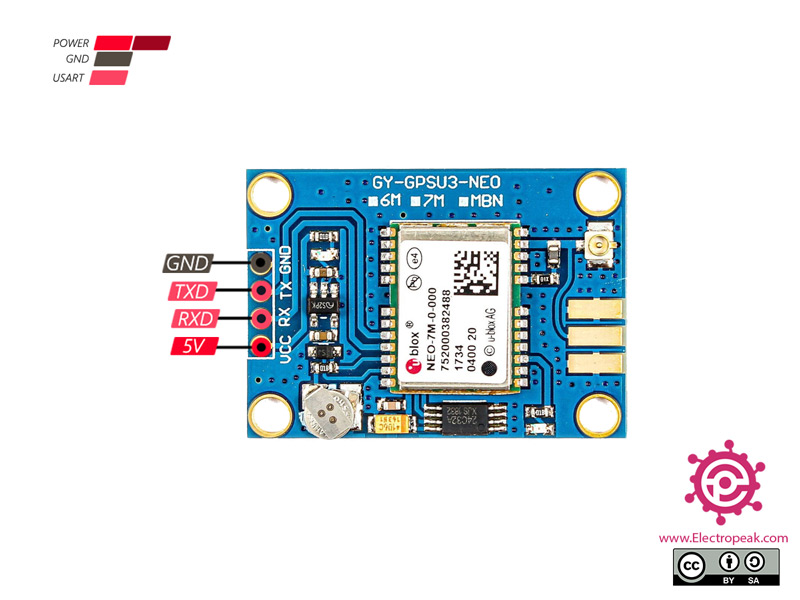
NEO-7M GPS Module Pinout
This sensor has 4 pins:
- VIN: Module power supply – 5 V
- GND: Ground
- RX: Receive data via serial protocol
- TX: Sending data via serial protocol
You can see pinout of this module in the image below.
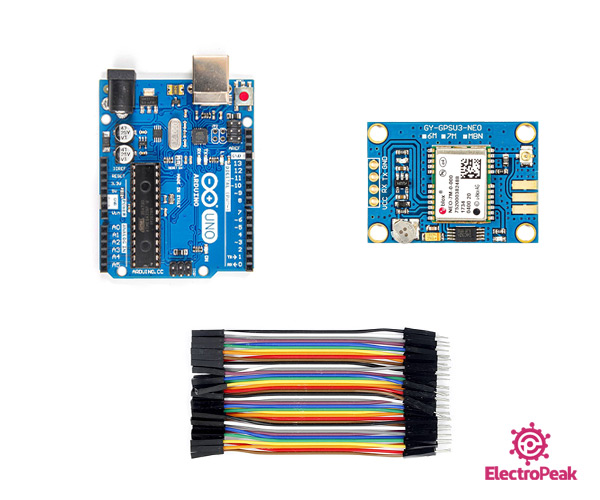
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Interfacing NEO-7M GPS Module with Arduino
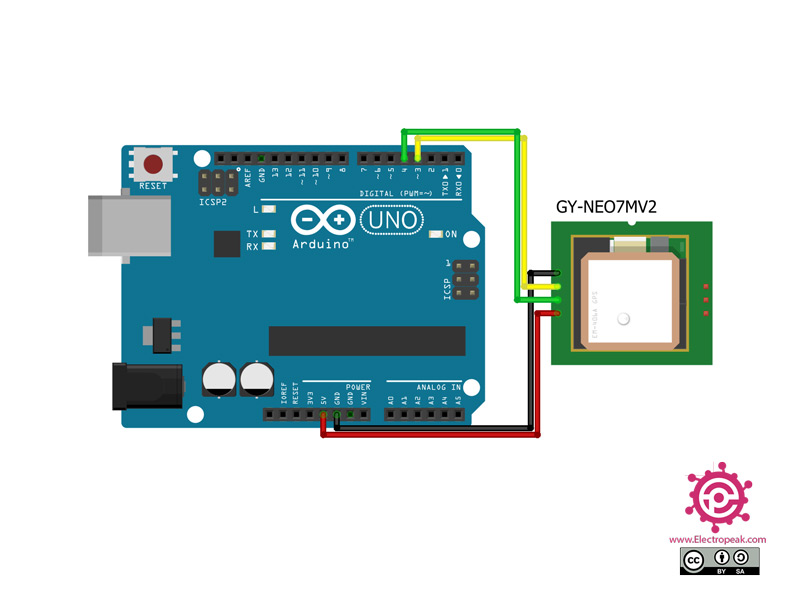
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit shows how you should connect Arduino to NEO-7M module. Connect wires accordingly.
Step 2: Code
Install the following library on your Arduino.
Tip
If you need more help with installing a library on Arduino, read this tutorial: How to Install an Arduino Library
Upload the following code to your Arduino.
/*
modified on Sep 27, 2020
Modified by MohammedDamirchi from https://github.com/mikalhart/TinyGPSPlus
Home
*/
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
/*
This sample sketch demonstrates the normal use of a TinyGPS++ (TinyGPSPlus) object.
It requires the use of SoftwareSerial, and assumes that you have a
9600-baud serial GPS device hooked up on pins 4(rx) and 3(tx).
*/
static const int RXPin = 3, TXPin = 4;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// The serial connection to the GPS device
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.println(F("DeviceExample.ino"));
Serial.println(F("A simple demonstration of TinyGPS++ with an attached GPS module"));
Serial.print(F("Testing TinyGPS++ library v. ")); Serial.println(TinyGPSPlus::libraryVersion());
Serial.println(F("by Mikal Hart"));
Serial.println();
}
void loop()
{
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
while (ss.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode(ss.read()))
displayInfo();
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
Serial.println(F("No GPS detected: check wiring."));
while(true);
}
}
void displayInfo()
{
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
if (gps.time.hour() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
}
else
{
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.println(); }
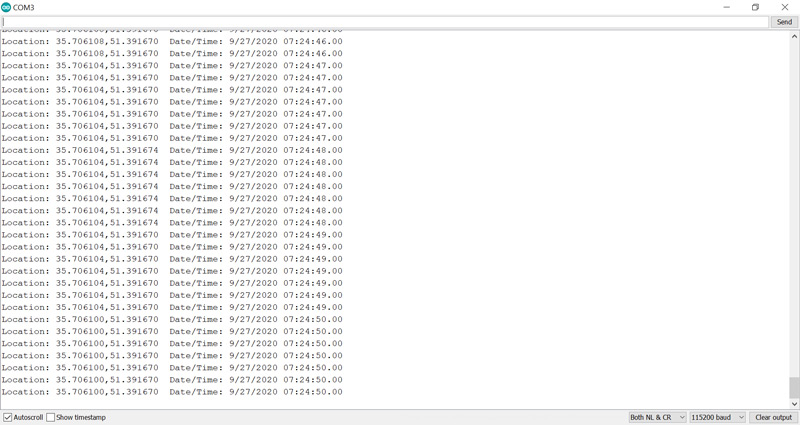
After uploading the code, you can see the output in the serial monitor.

Comments (12)
Hi
I just wanted to try out your code for my school project. But every time i try to get a signal, it alsways answers with “No GPS detected: please check wiring”. I know what it means and everything is connected properly. I think the problem is the antenna, but could there possibly be anything else wrong.
Hi,
Well, this is as use said most likely because of the antenna. But, there is also another thing you can check. Try the project outdoors. Actually, the NEO-7M GPS module works best when used in the open air. Also, wait for around 5 to 10 minutes after you power up the module since it usually takes a few minutes to connect to the GPS network.
the rx and tx pins are reversed in the diagram
Well, you seem to be correct! Thanks for your attention.
The problem is now solved by modifying line 14 of the code and changing the pin numbers assigned to Rx and Tx.
Hi The only thing I get back from the monitor is: $M&/�Ht�\Xn;�EVp��g�
Any ideas. GPS is blinking, jumers are oke.
Hi
check your serial baudrate please
it should be 115200
How can i set it to 10Hz mode?
hi peter
Normally, the library doesn’t support the “update rate mode.”
Before library configuration, you can adjust the “update rate mode” by the
GSMSerial.println("$PMTK220,100")commandThe ublox NEO 6,7,8 GPS modules are 3.3v devices. They should NOT be powered directly from the arduino 5v supply. Use the 3.3v output instead !!!!!
Hi Smurfy,
Thank you for your notice. If you examine the PCB for these models, you’ll notice they incorporate an LDO regulator to stabilize the voltage at 3.3 volts for the IC.
Hi,
The sketch is running and the date is correct but the time is off by 2 hours and location is coming in as invalid.
Any tips on what I need to do to fix this?
Thanks!!
Hi Jeff,
The time is based on GMT, so you’ll need to adjust the time zone according to your location.
For the module to connect to satellites, it generally needs to run for 1-2 minutes in an open space. If you’re indoors, try placing it near a window with a clear view of the sky. It may take up to 10 minutes to establish a connection.