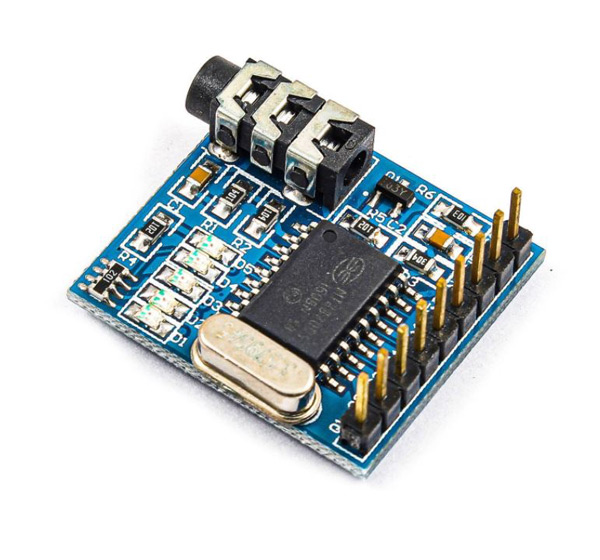
MT8870 DTMF Decoder Module Features
DTMF stands for Dual-tone-multi-frequency. This module is for sending signals using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines to switching centers. This module has two important applications: First, to specify the desired number to telecommunication through switching centers; second, it is capable of transmitting commands to these centers and other telecommunication devices.
Technical specifications:
- Input voltage: 5V
- 5mm input jack
- LED to indicate the binary outputs status
- Recognize numbers 0-9, letters A-D and symbols *, #
MT8870 DTMF Decoder Module Pinout
This module has 6 pins:
- VCC: Module power supply
- GND: Ground
- Q[1-4]: Binary Output
- EST: Early Steering (Output)
- INH: Inhibit (Input)
- TOE: Three State Output Enable (Input)
You can see the pinout of this module here.
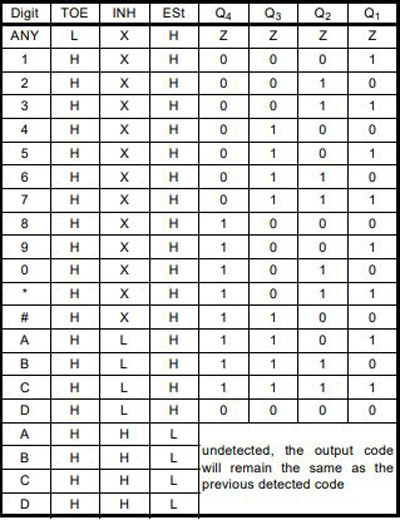
Different modes in each pin represent different data. The following table shows different modes:
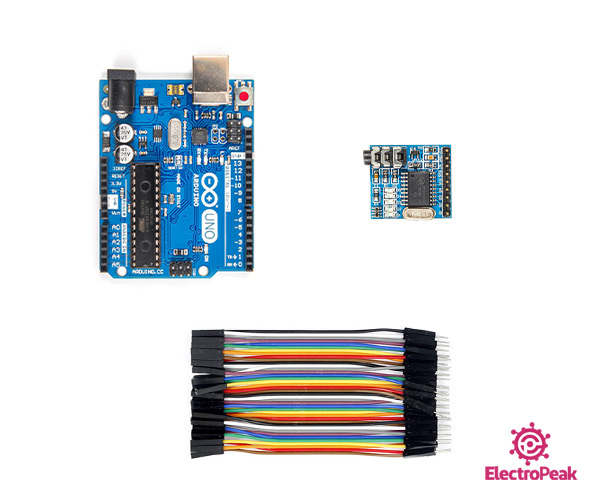
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Note
You need an AUX cable to interface this module.
Interfacing MT8870 DTMF Decoder Module with Arduino
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit shows how you should connect MT8870 module to Arduino and to the mobile phone using the AUX cable. Connect wires accordingly.
Step 2: Code
Upload the following code to your Arduino.
/*
MT8870-DTMF-Receiver-Module
Made on 09 Feb, 2021
Home
*/
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(3, INPUT);
pinMode(4, INPUT);
pinMode(5, INPUT);
pinMode(6, INPUT);
pinMode(7, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
uint8_t number;
bool signal;
signal = digitalRead(7);
if (signal == HIGH) /*When DTMF tone is detected, STQ will read HIGH for the duration of the tone*/
{
delay(100);
number = ( 0x00 | (digitalRead(3) << 0) | (digitalRead(4) << 1) | (digitalRead(5) << 2) | (digitalRead(6) << 3) );
switch (number)
{
case 0x01:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 1");
break;
case 0x02:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 2");
break;
case 0x03:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 3");
break;
case 0x04:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 4");
break;
case 0x05:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 5");
break;
case 0x06:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 6");
break;
case 7:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 7");
break;
case 0x08:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 8");
break;
case 0x09:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 9");
break;
case 0x0A:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: 0");
break;
case 0x0B:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: *");
break;
case 0x0C:
Serial.println("Pin Pressed: #");
break;
}
}
}
In this program, you can evaluate the performance of this module using the mobile keyboard. By touching each number 0 to 9 and also the # and * symbols, you can see them in the Serial Monitor.
The output is as follows: