GY-271 Compass Module Features
Magnetic current and field have directly relation with each other. When current flows in a wire (electrons start travelling in one direction), a magnetic field is created. The main idea of compass sensors is based on this relationship. The direction of the earth’s magnetic field affects the flow of electrons in the sensor. By measuring these changes in current, the sensor will be able to detect direction.
The GY-271 module uses the QMC5883L chip to detect magnetic fields and its directions. The communication protocol of this module is I2C and you can connect it to different processors such as Arduino boards using two SCL and SDA pins.
You can download the QMC5883L chip datasheet here.
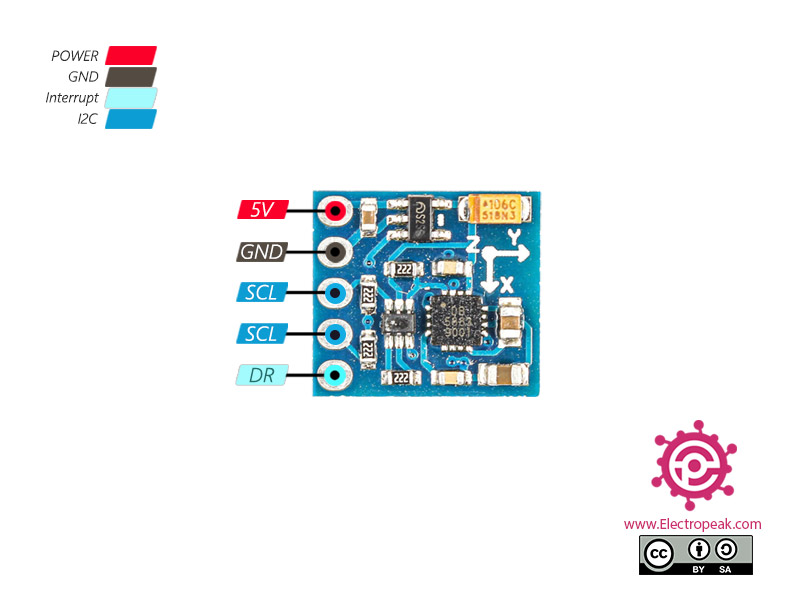
GY-271 Compass Module Pinout
GY-271 Module has 5 pins. The application of them is as follows:
- VCC: Module power supply – 3 to 5 volts
- GND: Ground
- SCL: I2C Clock pin
- SDA: I2C Data pin
- DRDY (DataReady): When the output value of the sensor is ready, an interrupt occurs in this pin. This pin is pulled up inside the module by default. When the output value of the module is ready, the pin is “0” for 250 microseconds.
You can see the pinout of this module in the followugn figure.
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Interfacing GY-271 (QMC5883L) Compass with Arduino
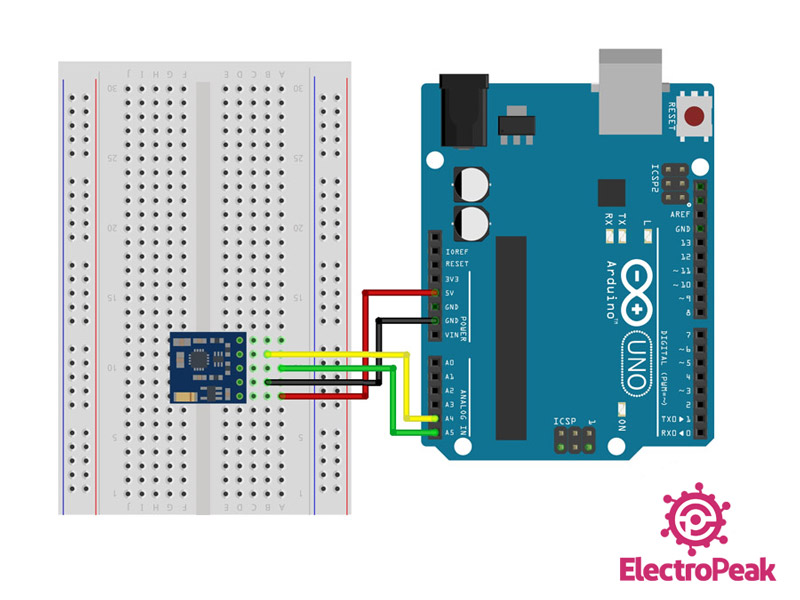
Step 1: Circuit
Connect the module to Arduino according to the following diagram
Step 2: Installing the library
Download the module library from this link and install it.
Note
This library has a variety of examples for interfacing a compass module. You can also use those examples.
Step 3: Code
After installing the library, upload the following code to your Arduino board. Then open the serial monitor to display the compass output.
/*
GY-271 Compass
modified on 02 Sep 2020
by Mohammad Reza Akbari @ Electropeak
Home
*/
// I2C Library
#include <Wire.h>
// QMC5883L Compass Library
#include <QMC5883LCompass.h>
QMC5883LCompass compass;
void setup() {
// Initialize the serial port.
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize I2C.
Wire.begin();
// Initialize the Compass.
compass.init();
}
void loop() {
int x, y, z;
// Read compass values
compass.read();
x = compass.getX();
y = compass.getY();
z = compass.getZ();
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" Y: ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" Z: ");
Serial.println(z);
delay(300);
}


Comments (6)
The figure that should show the circuit does not work.
Hi Joselin,
What seems to be the issue?
missing diagram
Thank you, It’s been updated.
I’m sorry but I’ve problem. x,y,z values are all 0 .
Hi Aria,
First, ensure your wiring is correct. You can use the I2C Scanner to confirm if everything is connected properly.
Then, compare the ID obtained from the I2C Scanner with the ID specified in the library.