APC220 Wireless Data Communication Module Features
Electronic devices need to be connected wirelessly in so many cases. In these cases, Radio Frequency or RF equipments are used. RF modules include all radio waves that can travel different distances and reach the receiver according to their frequency and amplitude.
The APC220 module uses UART / TTL for communication. This module comes with a USB to TTL converter that you can use to connect the module directly to your system and connect the second module to a microcontroller. This module offers a wide range for communication over long distances, so, it is recommended to use in robots.
Download the datasheet of this module here.
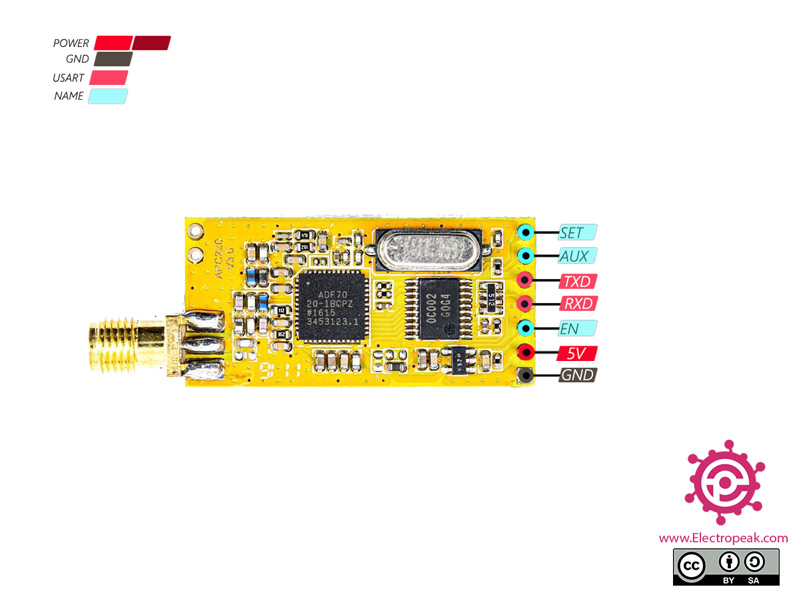
APC220 Wireless Data Communication Module Pinout
This module has 7 pins:
- VIN: Module power supply
- GND: Ground
- RX: Data receive through serial protocol
- TX: Data transmit through serial protocol
- SET: Mode Setting
- AUX: For other commands
- EN: Enable module
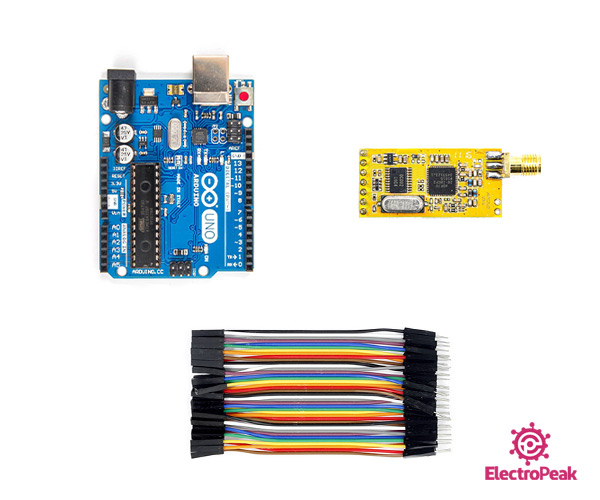
Required Materials
Hardware Components
Software Apps
Interfacing APC220 Wireless Data Communication Module with Arduino
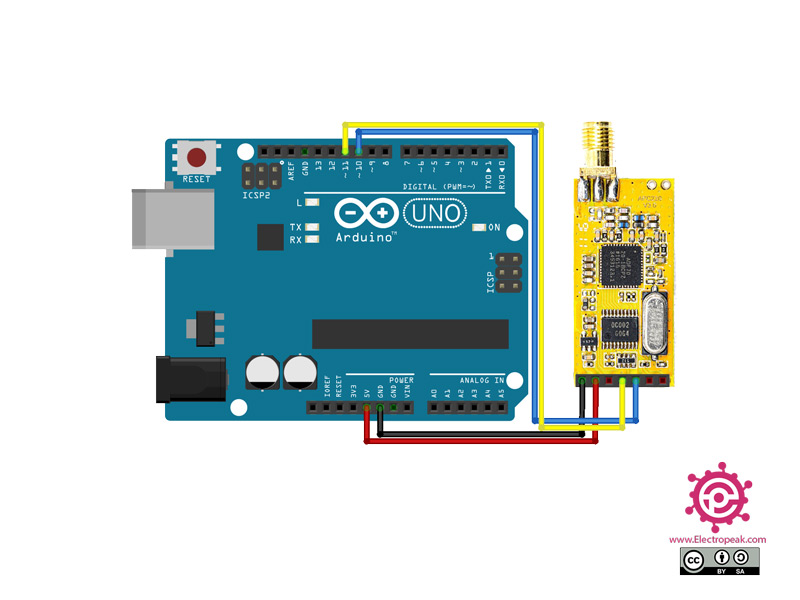
Step 1: Circuit
The following circuit shows how you should connect the Arduino to the APC220 module. Connect wires accordingly.
Note
If the connection is not established, you can replace the RX and TX wires.
Connect the second module to your system using the converter.
Step 2: Library
Install the following library on your Arduino IDE.
Tip
If you need more help with installing a library on Arduino, read this tutorial: How to Install an Arduino Library
Step 3: Code
Upload the following code to your Arduino.
/*
Modified on March 09, 2021
Modified by MohammedDamirchi from https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/SoftwareSerial
Home
*/
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
// set the data rate for the SoftwareSerial port
mySerial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() { // run over and over
if (mySerial.available()) {
Serial.write(mySerial.read());
}
if (Serial.available()) {
mySerial.write(Serial.read());
}
}
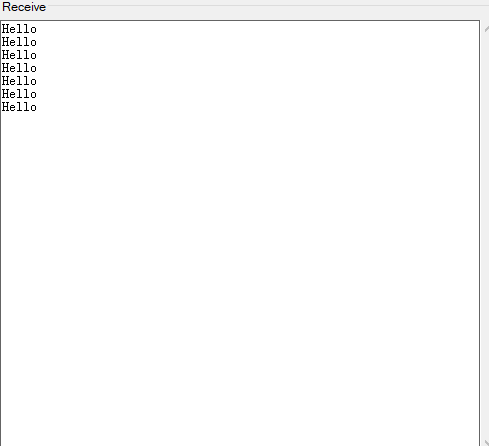
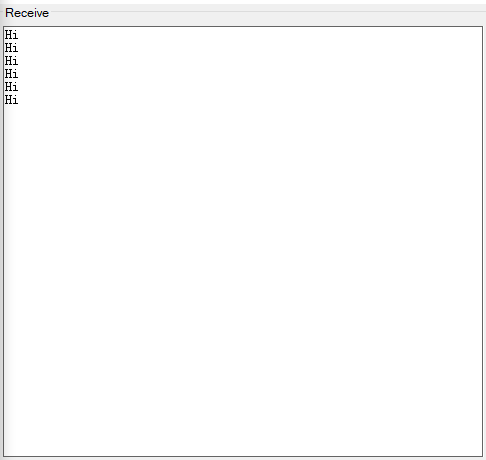
This code is for testing the connection between the Arduino and your system.
Now open the serial monitors of the Arduino IDE and the converter. By sending data on each side, you can observe the data on the other side.
Note
The Serial Monitor baud rate is 9600 on both sides by default.